Arctic Ocean on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The Arctic Ocean is the smallest and shallowest of the world's five major oceans. It spans an area of approximately and is known as the coldest of all the oceans. The International Hydrographic Organization (IHO) recognizes it as an ocean, although some oceanographers call it the Arctic Mediterranean Sea. It has been described approximately as an estuary of the Atlantic Ocean. It is also seen as the northernmost part of the all-encompassing World Ocean.
The Arctic Ocean includes the North Pole region in the middle of the Northern Hemisphere and extends south to about 60°N. The Arctic Ocean is surrounded by Eurasia and
The Arctic Ocean is the smallest and shallowest of the world's five major oceans. It spans an area of approximately and is known as the coldest of all the oceans. The International Hydrographic Organization (IHO) recognizes it as an ocean, although some oceanographers call it the Arctic Mediterranean Sea. It has been described approximately as an estuary of the Atlantic Ocean. It is also seen as the northernmost part of the all-encompassing World Ocean.
The Arctic Ocean includes the North Pole region in the middle of the Northern Hemisphere and extends south to about 60°N. The Arctic Ocean is surrounded by Eurasia and 
 Early Paleo-Eskimo groups included the Pre-Dorset (); the Saqqaq culture of Greenland (2500–800 BC); the
Early Paleo-Eskimo groups included the Pre-Dorset (); the Saqqaq culture of Greenland (2500–800 BC); the
 Early cartographers were unsure whether to draw the region around the North Pole as land (as in
Early cartographers were unsure whether to draw the region around the North Pole as land (as in 

. CIA World Fact Book * Alaska ** Utqiaġvik (Barrow) ** Prudhoe Bay * Canada ** Manitoba: Churchill ( Port of Churchill) **
 In large parts of the Arctic Ocean, the top layer (about ) is of lower salinity and lower temperature than the rest. It remains relatively stable because the salinity effect on density is bigger than the temperature effect. It is fed by the freshwater input of the big Siberian and Canadian rivers ( Ob, Yenisei, Lena, Mackenzie), the water of which quasi floats on the saltier, denser, deeper ocean water. Between this lower salinity layer and the bulk of the ocean lies the so-called halocline, in which both salinity and temperature rise with increasing depth.
In large parts of the Arctic Ocean, the top layer (about ) is of lower salinity and lower temperature than the rest. It remains relatively stable because the salinity effect on density is bigger than the temperature effect. It is fed by the freshwater input of the big Siberian and Canadian rivers ( Ob, Yenisei, Lena, Mackenzie), the water of which quasi floats on the saltier, denser, deeper ocean water. Between this lower salinity layer and the bulk of the ocean lies the so-called halocline, in which both salinity and temperature rise with increasing depth.
 Because of its relative isolation from other oceans, the Arctic Ocean has a uniquely complex system of water flow. It resembles some hydrological features of the Mediterranean Sea, referring to its deep waters having only limited communication through the Fram Strait with the Atlantic Basin, "where the circulation is dominated by thermohaline forcing". egional Oceanography: An Introduction. Tomczak, Godfrey. Retrieved 18 November 2013./ref> The Arctic Ocean has a total volume of 18.07 × 106 km3, equal to about 1.3% of the World Ocean. Mean surface circulation is predominantly cyclonic on the Eurasian side and anticyclonic in the Canadian Basin.
Water enters from both the Pacific and Atlantic Oceans and can be divided into three unique water masses. The deepest water mass is called Arctic Bottom Water and begins around depth. It is composed of the densest water in the World Ocean and has two main sources: Arctic shelf water and Greenland Sea Deep Water. Water in the shelf region that begins as inflow from the Pacific passes through the narrow Bering Strait at an average rate of 0.8 Sverdrups and reaches the
Because of its relative isolation from other oceans, the Arctic Ocean has a uniquely complex system of water flow. It resembles some hydrological features of the Mediterranean Sea, referring to its deep waters having only limited communication through the Fram Strait with the Atlantic Basin, "where the circulation is dominated by thermohaline forcing". egional Oceanography: An Introduction. Tomczak, Godfrey. Retrieved 18 November 2013./ref> The Arctic Ocean has a total volume of 18.07 × 106 km3, equal to about 1.3% of the World Ocean. Mean surface circulation is predominantly cyclonic on the Eurasian side and anticyclonic in the Canadian Basin.
Water enters from both the Pacific and Atlantic Oceans and can be divided into three unique water masses. The deepest water mass is called Arctic Bottom Water and begins around depth. It is composed of the densest water in the World Ocean and has two main sources: Arctic shelf water and Greenland Sea Deep Water. Water in the shelf region that begins as inflow from the Pacific passes through the narrow Bering Strait at an average rate of 0.8 Sverdrups and reaches the
. Polar Discovery This water is met by Greenland Sea Deep Water, which forms during the passage of winter storms. As temperatures cool dramatically in the winter, ice forms, and intense vertical convection allows the water to become dense enough to sink below the warm saline water below. Arctic Bottom Water is critically important because of its outflow, which contributes to the formation of Atlantic Deep Water. The overturning of this water plays a key role in global circulation and the moderation of climate.
In the depth range of is a water mass referred to as Atlantic Water. Inflow from the North Atlantic Current enters through the Fram Strait, cooling and sinking to form the deepest layer of the halocline, where it circles the Arctic Basin counter-clockwise. This is the highest volumetric inflow to the Arctic Ocean, equalling about 10 times that of the Pacific inflow, and it creates the Arctic Ocean Boundary Current. It flows slowly, at about 0.02 m/s. Atlantic Water has the same salinity as Arctic Bottom Water but is much warmer (up to ). In fact, this water mass is actually warmer than the surface water and remains submerged only due to the role of salinity in density. When water reaches the basin, it is pushed by strong winds into a large circular current called the Beaufort Gyre. Water in the Beaufort Gyre is far less saline than that of the Chukchi Sea due to inflow from large Canadian and Siberian rivers.
The final defined water mass in the Arctic Ocean is called Arctic Surface Water and is found in the depth range of . The most important feature of this water mass is a section referred to as the sub-surface layer. It is a product of Atlantic water that enters through canyons and is subjected to intense mixing on the Siberian Shelf. As it is entrained, it cools and acts a heat shield for the surface layer on account of weak mixing between layers.
However, over the past couple of decades a combination of the warming and the shoaling of Atlantic water are leading to the increasing influence of Atlantic water heat in melting sea ice in the eastern Arctic. The most recent estimates, for 2016–2018, indicate the oceanic heat flux to the surface has now overtaken the atmospheric flux in the eastern Eurasian Basin. Over the same period the weakening halocline stratification has coincided with increasing upper ocean currents thought to be associated with declining sea ice, indicate increasing mixing in this region. In contrast direct measurements of mixing in the western Arctic indicate the Atlantic water heat remains isolated at intermediate depths even under the 'perfect storm' conditions of the
This water is met by Greenland Sea Deep Water, which forms during the passage of winter storms. As temperatures cool dramatically in the winter, ice forms, and intense vertical convection allows the water to become dense enough to sink below the warm saline water below. Arctic Bottom Water is critically important because of its outflow, which contributes to the formation of Atlantic Deep Water. The overturning of this water plays a key role in global circulation and the moderation of climate.
In the depth range of is a water mass referred to as Atlantic Water. Inflow from the North Atlantic Current enters through the Fram Strait, cooling and sinking to form the deepest layer of the halocline, where it circles the Arctic Basin counter-clockwise. This is the highest volumetric inflow to the Arctic Ocean, equalling about 10 times that of the Pacific inflow, and it creates the Arctic Ocean Boundary Current. It flows slowly, at about 0.02 m/s. Atlantic Water has the same salinity as Arctic Bottom Water but is much warmer (up to ). In fact, this water mass is actually warmer than the surface water and remains submerged only due to the role of salinity in density. When water reaches the basin, it is pushed by strong winds into a large circular current called the Beaufort Gyre. Water in the Beaufort Gyre is far less saline than that of the Chukchi Sea due to inflow from large Canadian and Siberian rivers.
The final defined water mass in the Arctic Ocean is called Arctic Surface Water and is found in the depth range of . The most important feature of this water mass is a section referred to as the sub-surface layer. It is a product of Atlantic water that enters through canyons and is subjected to intense mixing on the Siberian Shelf. As it is entrained, it cools and acts a heat shield for the surface layer on account of weak mixing between layers.
However, over the past couple of decades a combination of the warming and the shoaling of Atlantic water are leading to the increasing influence of Atlantic water heat in melting sea ice in the eastern Arctic. The most recent estimates, for 2016–2018, indicate the oceanic heat flux to the surface has now overtaken the atmospheric flux in the eastern Eurasian Basin. Over the same period the weakening halocline stratification has coincided with increasing upper ocean currents thought to be associated with declining sea ice, indicate increasing mixing in this region. In contrast direct measurements of mixing in the western Arctic indicate the Atlantic water heat remains isolated at intermediate depths even under the 'perfect storm' conditions of the
 Much of the Arctic Ocean is covered by sea ice that varies in extent and thickness seasonally. The mean extent of the Arctic sea ice has been continuously decreasing in the last decades, declining at a rate of currently 12.85% per decade since 1980 from the average winter value of . The seasonal variations are about , with the maximum in April and minimum in September. The sea ice is affected by wind and ocean currents, which can move and rotate very large areas of ice. Zones of compression also arise, where the ice piles up to form pack ice.
Much of the Arctic Ocean is covered by sea ice that varies in extent and thickness seasonally. The mean extent of the Arctic sea ice has been continuously decreasing in the last decades, declining at a rate of currently 12.85% per decade since 1980 from the average winter value of . The seasonal variations are about , with the maximum in April and minimum in September. The sea ice is affected by wind and ocean currents, which can move and rotate very large areas of ice. Zones of compression also arise, where the ice piles up to form pack ice.
 Due to the pronounced seasonality of 2–6 months of midnight sun and polar night in the Arctic Ocean, the primary production of photosynthesizing organisms such as ice algae and
Due to the pronounced seasonality of 2–6 months of midnight sun and polar night in the Arctic Ocean, the primary production of photosynthesizing organisms such as ice algae and 

Richard Black, 7 October 2005. BBC News. Retrieved 7 December 2006. Research shows that the Arctic may become ice-free in the summer for the first time in human history by 2040. Estimates vary for when the last time the Arctic was ice-free: 65 million years ago when fossils indicate that plants existed there to as recently as 5,500 years ago; ice and ocean cores going back 8,000 years to the last warm period or 125,000 during the last intraglacial period. Warming temperatures in the Arctic may cause large amounts of fresh melt-water to enter the north Atlantic, possibly disrupting global ocean current patterns. Potentially severe changes in the Earth's climate might then ensue. As the extent of sea ice diminishes and sea level rises, the effect of storms such as the
Arctic Council
Arctic Environmental Atlas
Interactive map
Arctic Great Rivers Observatory (ArcticGRO)
Arctic Ocean
'' The World Factbook''. Central Intelligence Agency.
Daily Arctic Ocean Rawinsonde Data from Soviet Drifting Ice Stations (1954–1990)
at NSIDC
Images from Web Cams deployed in spring on an ice floe
Data from instruments deployed on an ice floe
International Polar Foundation
* {{Authority control several islands Oceans Extreme points of Earth Articles containing video clips Geography of Northeast Asia Geography of Northern Europe Geography of Eastern Europe Geography of North America Seas of the United States Seas of Canada Seas of Greenland Seas of Norway Seas of Russia
 The Arctic Ocean is the smallest and shallowest of the world's five major oceans. It spans an area of approximately and is known as the coldest of all the oceans. The International Hydrographic Organization (IHO) recognizes it as an ocean, although some oceanographers call it the Arctic Mediterranean Sea. It has been described approximately as an estuary of the Atlantic Ocean. It is also seen as the northernmost part of the all-encompassing World Ocean.
The Arctic Ocean includes the North Pole region in the middle of the Northern Hemisphere and extends south to about 60°N. The Arctic Ocean is surrounded by Eurasia and
The Arctic Ocean is the smallest and shallowest of the world's five major oceans. It spans an area of approximately and is known as the coldest of all the oceans. The International Hydrographic Organization (IHO) recognizes it as an ocean, although some oceanographers call it the Arctic Mediterranean Sea. It has been described approximately as an estuary of the Atlantic Ocean. It is also seen as the northernmost part of the all-encompassing World Ocean.
The Arctic Ocean includes the North Pole region in the middle of the Northern Hemisphere and extends south to about 60°N. The Arctic Ocean is surrounded by Eurasia and North America
North America is a continent in the Northern Hemisphere and almost entirely within the Western Hemisphere. It is bordered to the north by the Arctic Ocean, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, to the southeast by South America and the Car ...
, and the borders follow topographic features: the Bering Strait on the Pacific side and the Greenland Scotland Ridge on the Atlantic side. It is mostly covered by sea ice
Sea ice arises as seawater freezes. Because ice is less dense than water, it floats on the ocean's surface (as does fresh water ice, which has an even lower density). Sea ice covers about 7% of the Earth's surface and about 12% of the world's oce ...
throughout the year and almost completely in winter. The Arctic Ocean's surface temperature Surface temperature is the temperature at a surface.
Specifically, it may refer to:
* Surface air temperature, the temperature of the air near the surface of the earth
* Sea surface temperature, the temperature of water close to the ocean's sur ...
and salinity
Salinity () is the saltiness or amount of salt dissolved in a body of water, called saline water (see also soil salinity). It is usually measured in g/L or g/kg (grams of salt per liter/kilogram of water; the latter is dimensionless and equal ...
vary seasonally as the ice cover melts and freezes; its salinity is the lowest on average of the five major oceans, due to low evaporation
Evaporation is a type of vaporization that occurs on the surface of a liquid as it changes into the gas phase. High concentration of the evaporating substance in the surrounding gas significantly slows down evaporation, such as when humidi ...
, heavy fresh water
Fresh water or freshwater is any naturally occurring liquid or frozen water containing low concentrations of dissolved salts and other total dissolved solids. Although the term specifically excludes seawater and brackish water, it does include ...
inflow from rivers and streams, and limited connection and outflow to surrounding oceanic waters with higher salinities. The summer shrinking of the ice has been quoted at 50%. The US National Snow and Ice Data Center
The National Snow and Ice Data Center (NSIDC) is a United States information and referral center in support of polar and cryospheric research. NSIDC archives and distributes digital and analog snow and ice data and also maintains information abo ...
(NSIDC) uses satellite data to provide a daily record of Arctic sea ice cover and the rate of melting compared to an average period and specific past years, showing a continuous decline in sea ice extent. In September 2012, the Arctic ice extent reached a new record minimum. Compared to the average extent (1979–2000), the sea ice had diminished by 49%.

History
North America
Human habitation in the North American polar region goes back at least 17,000–50,000 years, during the Wisconsin glaciation. At this time, falling sea levels allowed people to move across the Bering land bridge that joined Siberia to northwestern North America (Alaska), leading to the Settlement of the Americas. Early Paleo-Eskimo groups included the Pre-Dorset (); the Saqqaq culture of Greenland (2500–800 BC); the
Early Paleo-Eskimo groups included the Pre-Dorset (); the Saqqaq culture of Greenland (2500–800 BC); the Independence I
Independence I was a culture of Paleo-Eskimos who lived in northern Greenland and the Canadian Arctic between 2400 and 1900 BC. There has been much debate among scholars on when Independence I culture disappeared, and, therefore, there is a margin ...
and Independence II cultures of northeastern Canada and Greenland ( and ); and the Groswater of Labrador and Nunavik
Nunavik (; ; iu, ᓄᓇᕕᒃ) comprises the northern third of the province of Quebec, part of the Nord-du-Québec region and nearly coterminous with Kativik. Covering a land area of north of the 55th parallel, it is the homeland of the I ...
. The Dorset culture spread across Arctic North America between 500 BC and AD 1500. The Dorset were the last major Paleo-Eskimo culture in the Arctic before the migration east from present-day Alaska of the Thule, the ancestors of the modern Inuit.
The Thule Tradition
The Thule (, , ) or proto-Inuit were the ancestors of all modern Inuit. They developed in coastal Alaska by the year 1000 and expanded eastward across northern Canada, reaching Greenland by the 13th century. In the process, they replaced people o ...
lasted from about 200 BC to AD 1600, arising around the Bering Strait and later encompassing almost the entire Arctic region of North America. The Thule people were the ancestors of the Inuit, who now live in Alaska, Northwest Territories
The Northwest Territories (abbreviated ''NT'' or ''NWT''; french: Territoires du Nord-Ouest, formerly ''North-Western Territory'' and ''North-West Territories'' and namely shortened as ''Northwest Territory'') is a federal territory of Canada. ...
, Nunavut
Nunavut ( , ; iu, ᓄᓇᕗᑦ , ; ) is the largest and northernmost Provinces and territories of Canada#Territories, territory of Canada. It was separated officially from the Northwest Territories on April 1, 1999, via the ''Nunavut Act'' ...
, northern Quebec, Labrador and Greenland.
Europe
For much of European history, the northpolar region
The polar regions, also called the frigid geographical zone, zones or polar zones, of Earth are the regions of the planet that surround its geographical poles (the North Pole, North and South Poles), lying within the polar circles. These high l ...
s remained largely unexplored and their geography conjectural. Pytheas
Pytheas of Massalia (; Ancient Greek: Πυθέας ὁ Μασσαλιώτης ''Pythéas ho Massaliōtēs''; Latin: ''Pytheas Massiliensis''; born 350 BC, 320–306 BC) was a Greeks, Greek List of Graeco-Roman geographers, geographer, explor ...
of Massilia recorded an account of a journey northward in 325 BC, to a land he called " Eschate Thule", where the Sun only set for three hours each day and the water was replaced by a congealed substance "on which one can neither walk nor sail". He was probably describing loose sea ice known today as " growlers" or "bergy bits"; his "Thule" was probably Norway, though the Faroe Islands or Shetland
Shetland, also called the Shetland Islands and formerly Zetland, is a subarctic archipelago in Scotland lying between Orkney, the Faroe Islands and Norway. It is the northernmost region of the United Kingdom.
The islands lie about to the no ...
have also been suggested.
 Early cartographers were unsure whether to draw the region around the North Pole as land (as in
Early cartographers were unsure whether to draw the region around the North Pole as land (as in Johannes Ruysch
Johannes Ruysch (c. 1460? in Utrecht – 1533 in Cologne), a.k.a. ''Johann Ruijsch'' or ''Giovanni Ruisch'' was an explorer, cartographer, astronomer, manuscript illustrator and painter from the Low Countries who produced a famous map of the world ...
's map of 1507, or Gerardus Mercator
Gerardus Mercator (; 5 March 1512 – 2 December 1594) was a 16th-century geographer, cosmographer and cartographer from the County of Flanders. He is most renowned for creating the 1569 world map based on a new projection which represented ...
's map of 1595) or water (as with Martin Waldseemüller's world map of 1507). The fervent desire of European merchants for a northern passage, the Northern Sea Route or the Northwest Passage, to "Cathay
Cathay (; ) is a historical name for China that was used in Europe. During the early modern period, the term ''Cathay'' initially evolved as a term referring to what is now Northern China, completely separate and distinct from China, which ...
" (China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's most populous country, with a population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and ...
) caused water to win out, and by 1723 mapmakers such as Johann Homann featured an extensive "Oceanus Septentrionalis" at the northern edge of their charts.
The few expeditions to penetrate much beyond the Arctic Circle
The Arctic Circle is one of the two polar circles, and the most northerly of the five major circles of latitude as shown on maps of Earth. Its southern equivalent is the Antarctic Circle.
The Arctic Circle marks the southernmost latitude at w ...
in that era added only small islands, such as Novaya Zemlya
Novaya Zemlya (, also , ; rus, Но́вая Земля́, p=ˈnovəjə zʲɪmˈlʲa, ) is an archipelago in northern Russia. It is situated in the Arctic Ocean, in the extreme northeast of Europe, with Cape Flissingsky, on the northern island, ...
(11th century) and Spitzbergen
Svalbard ( , ), also known as Spitsbergen, or Spitzbergen, is a Norwegian archipelago in the Arctic Ocean. North of mainland Europe, it is about midway between the northern coast of Norway and the North Pole. The islands of the group range ...
(1596), though, since these were often surrounded by pack-ice
Drift ice, also called brash ice, is sea ice that is not attached to the shoreline or any other fixed object (shoals, grounded icebergs, etc.).Leppäranta, M. 2011. The Drift of Sea Ice. Berlin: Springer-Verlag. Unlike fast ice, which is "fastene ...
, their northern limits were not so clear. The makers of navigational charts, more conservative than some of the more fanciful cartographers, tended to leave the region blank, with only fragments of known coastline sketched in.

19th century
This lack of knowledge of what lay north of the shifting barrier of ice gave rise to a number of conjectures. In England and other European nations, themyth
Myth is a folklore genre consisting of Narrative, narratives that play a fundamental role in a society, such as foundational tales or Origin myth, origin myths. Since "myth" is widely used to imply that a story is not Objectivity (philosophy), ...
of an " Open Polar Sea" was persistent. John Barrow, longtime Second Secretary of the British Admiralty
The Admiralty was a department of the Government of the United Kingdom responsible for the command of the Royal Navy until 1964, historically under its titular head, the Lord High Admiral – one of the Great Officers of State. For much of it ...
, promoted exploration of the region from 1818 to 1845 in search of this.
In the United States in the 1850s and 1860s, the explorers Elisha Kane and Isaac Israel Hayes both claimed to have seen part of this elusive body of water. Even quite late in the century, the eminent authority Matthew Fontaine Maury included a description of the Open Polar Sea in his textbook ''The Physical Geography of the Sea'' (1883). Nevertheless, as all the explorers who travelled closer and closer to the pole reported, the polar ice cap is quite thick and persists year-round.
Fridtjof Nansen
Fridtjof Wedel-Jarlsberg Nansen (; 10 October 186113 May 1930) was a Norwegian polymath and Nobel Peace Prize laureate. He gained prominence at various points in his life as an explorer, scientist, diplomat, and humanitarian. He led the team t ...
was the first to make a nautical crossing of the Arctic Ocean, in 1896.
20th century
The first surface crossing of the ocean was led by Wally Herbert in 1969, in adog sled
A dog sled or dog sleigh is a sled pulled by one or more sled dogs used to travel over ice and through snow. Numerous types of sleds are used, depending on their function. They can be used for dog sled racing. Traditionally in Greenland and the e ...
expedition from Alaska to Svalbard
Svalbard ( , ), also known as Spitsbergen, or Spitzbergen, is a Norwegian archipelago in the Arctic Ocean. North of mainland Europe, it is about midway between the northern coast of Norway and the North Pole. The islands of the group range ...
, with air support. The first nautical transit of the north pole was made in 1958 by the submarine USS ''Nautilus'', and the first surface nautical transit occurred in 1977 by the icebreaker NS ''Arktika''.
Since 1937, Soviet and Russian manned drifting ice stations have extensively monitored the Arctic Ocean. Scientific settlements were established on the drift ice and carried thousands of kilometres by ice floes.
In World War II, the European region of the Arctic Ocean was heavily contested: the Allied commitment to resupply the Soviet Union via its northern ports was opposed by German naval and air forces.
Since 1954 commercial airlines have flown over the Arctic Ocean (see Polar route).
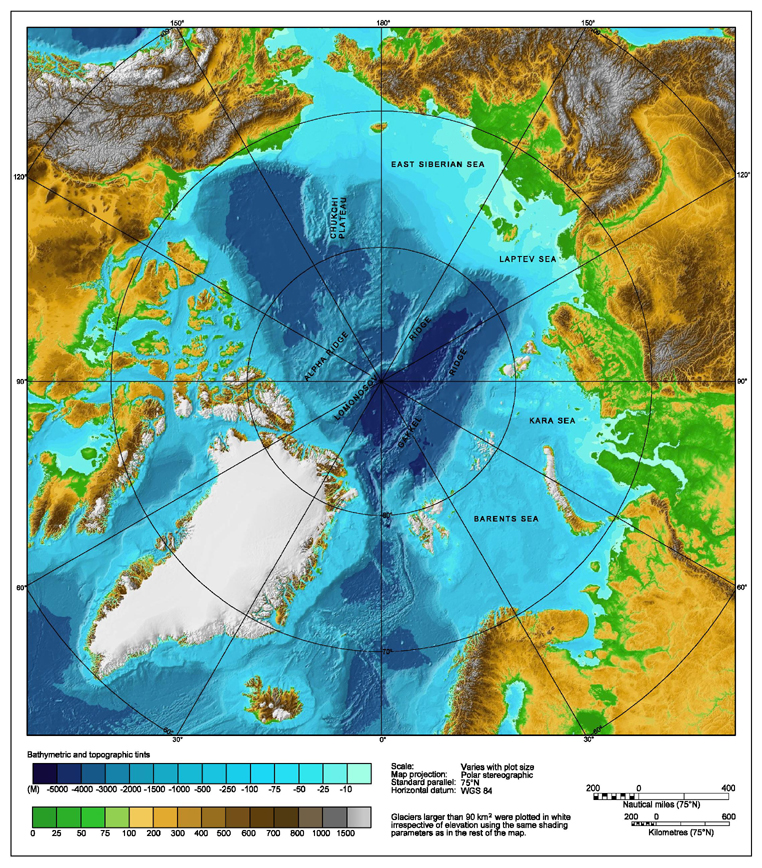
Geography

Size
The Arctic Ocean occupies a roughly circular basin and covers an area of about , almost the size of Antarctica. The coastline is long. It is the only ocean smaller than Russia, which has a land area of .Surrounding land and exclusive economic zones
The Arctic Ocean is surrounded by the land masses of Eurasia ( Russia and Norway), North America ( Canada and the U.S. state of Alaska), Greenland, and Iceland. Note: Some parts of the areas listed in the table are located in the Atlantic Ocean. Other consists of Gulfs,Strait
A strait is an oceanic landform connecting two seas or two other large areas of water. The surface water generally flows at the same elevation on both sides and through the strait in either direction. Most commonly, it is a narrow ocean channe ...
s, Channels and other parts without specific names and excludes Exclusive Economic Zones.
Subareas and connections
The Arctic Ocean is connected to the Pacific Ocean by the Bering Strait and to the Atlantic Ocean through theGreenland Sea
The Greenland Sea is a body of water that borders Greenland to the west, the Svalbard archipelago to the east, Fram Strait and the Arctic Ocean to the north, and the Norwegian Sea and Iceland to the south. The Greenland Sea is often defined as p ...
and Labrador Sea. (The Iceland Sea
The Iceland Sea is a small body of water delimited by the Jan Mayen fracture zone to the north, Greenland to the west, the Denmark Strait to the south, and the Jan Mayen Ridge to the east. Depths usually range from 500 to 2,000 meters but can be ...
is sometimes considered part of the Greenland Sea
The Greenland Sea is a body of water that borders Greenland to the west, the Svalbard archipelago to the east, Fram Strait and the Arctic Ocean to the north, and the Norwegian Sea and Iceland to the south. The Greenland Sea is often defined as p ...
, and sometimes separate.)
The largest seas in the Arctic Ocean:
# Barents Sea—1.4 million km2
# Hudson Bay
Hudson Bay ( crj, text=ᐐᓂᐯᒄ, translit=Wînipekw; crl, text=ᐐᓂᐹᒄ, translit=Wînipâkw; iu, text=ᑲᖏᖅᓱᐊᓗᒃ ᐃᓗᐊ, translit=Kangiqsualuk ilua or iu, text=ᑕᓯᐅᔭᕐᔪᐊᖅ, translit=Tasiujarjuaq; french: b ...
—1.23 million km2 (sometimes not included)
# Greenland Sea
The Greenland Sea is a body of water that borders Greenland to the west, the Svalbard archipelago to the east, Fram Strait and the Arctic Ocean to the north, and the Norwegian Sea and Iceland to the south. The Greenland Sea is often defined as p ...
—1.205 million km2
# East Siberian Sea
The East Siberian Sea ( rus, Восто́чно-Сиби́рское мо́ре, r=Vostochno-Sibirskoye more) is a marginal sea in the Arctic Ocean. It is located between the Arctic Cape to the north, the coast of Siberia to the south, the New Si ...
—987,000 km2
# Kara Sea—926,000 km2
# Laptev Sea—662,000 km2
# Chukchi Sea
Chukchi Sea ( rus, Чуко́тское мо́ре, r=Chukotskoye more, p=tɕʊˈkotskəjə ˈmorʲɪ), sometimes referred to as the Chuuk Sea, Chukotsk Sea or the Sea of Chukotsk, is a marginal sea of the Arctic Ocean. It is bounded on the west b ...
—620,000 km2
# Beaufort Sea
The Beaufort Sea (; french: Mer de Beaufort, Iñupiaq: ''Taġiuq'') is a marginal sea of the Arctic Ocean, located north of the Northwest Territories, the Yukon, and Alaska, and west of Canada's Arctic islands. The sea is named after Sir Fr ...
—476,000 km2
# Amundsen Gulf
# White Sea—90,000 km2
# Pechora Sea—81,263 km2
# Lincoln Sea—64,000 km2
# Prince Gustaf Adolf Sea
Prince Gustaf Adolf Sea formerly Prince Gustav Adolf Sea (french: Mer du Prince-Gustave-Adolphe) is a marginal sea of the Arctic Ocean located in the Qikiqtaaluk Region, Nunavut, and the Inuvik Region, Canada.
Geography
It is situated among the ...
# Queen Victoria Sea
# Wandel Sea
Different authorities put various marginal seas in either the Arctic Ocean or the Atlantic Ocean, including: Hudson Bay
Hudson Bay ( crj, text=ᐐᓂᐯᒄ, translit=Wînipekw; crl, text=ᐐᓂᐹᒄ, translit=Wînipâkw; iu, text=ᑲᖏᖅᓱᐊᓗᒃ ᐃᓗᐊ, translit=Kangiqsualuk ilua or iu, text=ᑕᓯᐅᔭᕐᔪᐊᖅ, translit=Tasiujarjuaq; french: b ...
,
Baffin Bay
Baffin Bay ( Inuktitut: ''Saknirutiak Imanga''; kl, Avannaata Imaa; french: Baie de Baffin), located between Baffin Island and the west coast of Greenland, is defined by the International Hydrographic Organization as a marginal sea of the Arct ...
, the Norwegian Sea, and Hudson Strait.
Islands
The main islands and archipelagos in the Arctic Ocean are, from the prime meridian west: * Jan Mayen (Norway) * Iceland * Greenland *Arctic Archipelago
The Arctic Archipelago, also known as the Canadian Arctic Archipelago, is an archipelago lying to the north of the Canadian continental mainland, excluding Greenland (an autonomous territory of Denmark).
Situated in the northern extremity of No ...
(Canada, includes the Queen Elizabeth Islands
The Queen Elizabeth Islands (french: Îles de la Reine-Élisabeth; formerly Parry Islands or Parry Archipelago) are the northernmost cluster of islands in Canada's Arctic Archipelago, split between Nunavut and the Northwest Territories in Northe ...
and Baffin Island
Baffin Island (formerly Baffin Land), in the Canadian territory of Nunavut, is the largest island in Canada and the fifth-largest island in the world. Its area is , slightly larger than Spain; its population was 13,039 as of the 2021 Canadia ...
)
* Wrangel Island (Russia)
* New Siberian Islands (Russia)
* Severnaya Zemlya (Russia)
* Novaya Zemlya
Novaya Zemlya (, also , ; rus, Но́вая Земля́, p=ˈnovəjə zʲɪmˈlʲa, ) is an archipelago in northern Russia. It is situated in the Arctic Ocean, in the extreme northeast of Europe, with Cape Flissingsky, on the northern island, ...
(Russia, includes Severny Island and Yuzhny Island)
* Franz Josef Land (Russia)
* Svalbard
Svalbard ( , ), also known as Spitsbergen, or Spitzbergen, is a Norwegian archipelago in the Arctic Ocean. North of mainland Europe, it is about midway between the northern coast of Norway and the North Pole. The islands of the group range ...
(Norway, including Bear Island))
Ports
There are several ports andharbour
A harbor (American English), harbour (British English; see spelling differences), or haven is a sheltered body of water where ships, boats, and barges can be docked. The term ''harbor'' is often used interchangeably with ''port'', which is a ...
s on the Arctic Ocean.Arctic Ocean. CIA World Fact Book * Alaska ** Utqiaġvik (Barrow) ** Prudhoe Bay * Canada ** Manitoba: Churchill ( Port of Churchill) **
Nunavut
Nunavut ( , ; iu, ᓄᓇᕗᑦ , ; ) is the largest and northernmost Provinces and territories of Canada#Territories, territory of Canada. It was separated officially from the Northwest Territories on April 1, 1999, via the ''Nunavut Act'' ...
: Nanisivik ( Nanisivik Naval Facility)
** Tuktoyaktuk and Inuvik
Inuvik (''place of man'') is the only town in the Inuvik Region, and the third largest community in Canada's Northwest Territories. Located in what is sometimes called the Beaufort Delta Region, it serves as its administrative and service cen ...
in the Northwest Territories
The Northwest Territories (abbreviated ''NT'' or ''NWT''; french: Territoires du Nord-Ouest, formerly ''North-Western Territory'' and ''North-West Territories'' and namely shortened as ''Northwest Territory'') is a federal territory of Canada. ...
* Greenland: Nuuk ( Nuuk Port and Harbour)
* Norway
** Mainland: Kirkenes
Kirkenes (; ; Skolt Sami: ''Ǩeârkknjargg;'' fi, Kirkkoniemi; ; russian: Киркенес) is a List of towns and cities in Norway, town in Sør-Varanger Municipality in Troms og Finnmark county, in the far northeastern part of Norway. The town ...
and Vardø
** Svalbard
Svalbard ( , ), also known as Spitsbergen, or Spitzbergen, is a Norwegian archipelago in the Arctic Ocean. North of mainland Europe, it is about midway between the northern coast of Norway and the North Pole. The islands of the group range ...
: Longyearbyen
Longyearbyen (, locally �lɔ̀ŋjɑrˌbyːən "The Longyear Town") is the world's northernmost settlement with a population greater than 1,000 and the largest inhabited area of Svalbard, Norway. It stretches along the foot of the left bank ...
* Iceland
** Akureyri
* Russia
** Barents Sea: Murmansk in the Barents Sea
** White Sea: Arkhangelsk
** Kara Sea: Labytnangi, Salekhard, Dudinka, Igarka and Dikson
** Laptev Sea: Tiksi in the
** East Siberian Sea: Pevek
Pevek (russian: Певе́к; Chukchi: , ''Pèèkin'' / ''Pèèk'') is an Arctic port town and the administrative center of Chaunsky District in Chukotka Autonomous Okrug, Russia, located on Chaunskaya Bay (part of the East Siberian Sea) on a peni ...
in the East Siberian Sea
Arctic shelves
The ocean's Arctic shelf comprises a number ofcontinental shelves
A continental shelf is a portion of a continent that is submerged under an area of relatively shallow water, known as a shelf sea. Much of these shelves were exposed by drops in sea level during glacial periods. The shelf surrounding an island ...
, including the Canadian Arctic shelf, underlying the Canadian Arctic Archipelago, and the Russian continental shelf, which is sometimes called the "Arctic Shelf" because it is larger. The Russian continental shelf consists of three separate, smaller shelves: the Barents Shelf, Chukchi Sea Shelf and Siberian Shelf. Of these three, the Siberian Shelf is the largest such shelf in the world; it holds large oil and gas reserves. The Chukchi shelf forms the border between Russian and the United States as stated in the USSR–USA Maritime Boundary Agreement
The Russia–United States maritime boundary was established by the June 1, 1990 USA/USSR Maritime Boundary Agreement (since Russia declared itself to be the successor of the Soviet Union). The United States Senate gave its advice and consent to ...
. The whole area is subject to international territorial claims
A land claim is defined as "the pursuit of recognized territorial ownership by a group or individual". The phrase is usually only used with respect to disputed or unresolved land claims. Some types of land claims include aboriginal land claims, A ...
.
The Chukchi Plateau extends from the Chukchi Sea Shelf.
Underwater features
An underwater ridge, theLomonosov Ridge
The Lomonosov Ridge (russian: Хребет Ломоносова, da, Lomonosovryggen) is an unusual underwater ridge of continental crust in the Arctic Ocean. It spans between the New Siberian Islands over the central part of the ocean to Elles ...
, divides the deep sea North Polar Basin into two oceanic basins: the Eurasian Basin, which is deep, and the Amerasian Basin (sometimes called the North American or Hyperborean Basin), which is about deep. The bathymetry of the ocean bottom is marked by fault block
Fault blocks are very large blocks of rock, sometimes hundreds of kilometres in extent, created by tectonic and localized stresses in Earth's crust. Large areas of bedrock are broken up into blocks by faults. Blocks are characterized by rela ...
ridges, abyssal plains, ocean deeps, and basins. The average depth of the Arctic Ocean is . The deepest point is Molloy Hole in the Fram Strait, at about .
The two major basins are further subdivided by ridges into the Canada Basin (between Beaufort Shelf of North America and the Alpha Ridge), Makarov Basin (between the Alpha and Lomonosov Ridges), Amundsen Basin
The Amundsen Basin, with depths up to , is the deepest abyssal plain in the Arctic Ocean, and contains the geographic North Pole. The Amundsen Basin is embraced by the Lomonosov Ridge (from to ) and the Gakkel Ridge (from to ). It is named after ...
(between Lomonosov and Gakkel ridges), and Nansen Basin (between the Gakkel Ridge and the continental shelf that includes the Franz Josef Land).
Geology
The crystalline basement rocks of mountains around the Arctic Ocean were recrystallized or formed during the Ellesmerian orogeny, the regional phase of the larger Caledonian orogeny in the Paleozoic Era. Regional subsidence in the Jurassic and Triassic periods led to significant sediment deposition, creating many of the reservoirs for current day oil and gas deposits. During the Cretaceous period, the Canadian Basin opened, and tectonic activity due to the assembly of Alaska caused hydrocarbons to migrate toward what is now Prudhoe Bay. At the same time, sediments shed off the rising Canadian Rockies built out the large Mackenzie Delta. The rifting apart of the supercontinent Pangea, beginning in the Triassic period, opened the early Atlantic Ocean. Rifting then extended northward, opening the Arctic Ocean as mafic oceanic crust material erupted out of a branch of Mid-Atlantic Ridge. The Amerasia Basin may have opened first, with the Chukchi Borderland moved along to the northeast by transform faults. Additional spreading helped to create the "triple-junction" of the Alpha-Mendeleev Ridge in the Late Cretaceous epoch. Throughout theCenozoic
The Cenozoic ( ; ) is Earth's current geological era, representing the last 66million years of Earth's history. It is characterised by the dominance of mammals, birds and flowering plants, a cooling and drying climate, and the current configura ...
Era, the subduction of the Pacific plate, the collision of India with Eurasia, and the continued opening of the North Atlantic created new hydrocarbon traps. The seafloor began spreading from the Gakkel Ridge in the Paleocene Epoch and the Eocene Epoch, causing the Lomonosov Ridge to move farther from land and subside.
Because of sea ice and remote conditions, the geology of the Arctic Ocean is still poorly explored. The Arctic Coring Expedition drilling shed some light on the Lomonosov Ridge, which appears to be continental crust separated from the Barents-Kara Shelf in the Paleocene and then starved of sediment. It may contain up to 10 billion barrels of oil. The Gakkel Ridge rift is also poorly understand and may extend into the Laptev Sea.
Oceanography
Water flow
 Because of its relative isolation from other oceans, the Arctic Ocean has a uniquely complex system of water flow. It resembles some hydrological features of the Mediterranean Sea, referring to its deep waters having only limited communication through the Fram Strait with the Atlantic Basin, "where the circulation is dominated by thermohaline forcing". egional Oceanography: An Introduction. Tomczak, Godfrey. Retrieved 18 November 2013./ref> The Arctic Ocean has a total volume of 18.07 × 106 km3, equal to about 1.3% of the World Ocean. Mean surface circulation is predominantly cyclonic on the Eurasian side and anticyclonic in the Canadian Basin.
Water enters from both the Pacific and Atlantic Oceans and can be divided into three unique water masses. The deepest water mass is called Arctic Bottom Water and begins around depth. It is composed of the densest water in the World Ocean and has two main sources: Arctic shelf water and Greenland Sea Deep Water. Water in the shelf region that begins as inflow from the Pacific passes through the narrow Bering Strait at an average rate of 0.8 Sverdrups and reaches the
Because of its relative isolation from other oceans, the Arctic Ocean has a uniquely complex system of water flow. It resembles some hydrological features of the Mediterranean Sea, referring to its deep waters having only limited communication through the Fram Strait with the Atlantic Basin, "where the circulation is dominated by thermohaline forcing". egional Oceanography: An Introduction. Tomczak, Godfrey. Retrieved 18 November 2013./ref> The Arctic Ocean has a total volume of 18.07 × 106 km3, equal to about 1.3% of the World Ocean. Mean surface circulation is predominantly cyclonic on the Eurasian side and anticyclonic in the Canadian Basin.
Water enters from both the Pacific and Atlantic Oceans and can be divided into three unique water masses. The deepest water mass is called Arctic Bottom Water and begins around depth. It is composed of the densest water in the World Ocean and has two main sources: Arctic shelf water and Greenland Sea Deep Water. Water in the shelf region that begins as inflow from the Pacific passes through the narrow Bering Strait at an average rate of 0.8 Sverdrups and reaches the Chukchi Sea
Chukchi Sea ( rus, Чуко́тское мо́ре, r=Chukotskoye more, p=tɕʊˈkotskəjə ˈmorʲɪ), sometimes referred to as the Chuuk Sea, Chukotsk Sea or the Sea of Chukotsk, is a marginal sea of the Arctic Ocean. It is bounded on the west b ...
. During the winter, cold Alaskan winds blow over the Chukchi Sea, freezing the surface water and pushing this newly formed ice out to the Pacific. The speed of the ice drift is roughly 1–4 cm/s. This process leaves dense, salty waters in the sea that sink over the continental shelf into the western Arctic Ocean and create a halocline.Arctic Ocean Circulation. Polar Discovery
 This water is met by Greenland Sea Deep Water, which forms during the passage of winter storms. As temperatures cool dramatically in the winter, ice forms, and intense vertical convection allows the water to become dense enough to sink below the warm saline water below. Arctic Bottom Water is critically important because of its outflow, which contributes to the formation of Atlantic Deep Water. The overturning of this water plays a key role in global circulation and the moderation of climate.
In the depth range of is a water mass referred to as Atlantic Water. Inflow from the North Atlantic Current enters through the Fram Strait, cooling and sinking to form the deepest layer of the halocline, where it circles the Arctic Basin counter-clockwise. This is the highest volumetric inflow to the Arctic Ocean, equalling about 10 times that of the Pacific inflow, and it creates the Arctic Ocean Boundary Current. It flows slowly, at about 0.02 m/s. Atlantic Water has the same salinity as Arctic Bottom Water but is much warmer (up to ). In fact, this water mass is actually warmer than the surface water and remains submerged only due to the role of salinity in density. When water reaches the basin, it is pushed by strong winds into a large circular current called the Beaufort Gyre. Water in the Beaufort Gyre is far less saline than that of the Chukchi Sea due to inflow from large Canadian and Siberian rivers.
The final defined water mass in the Arctic Ocean is called Arctic Surface Water and is found in the depth range of . The most important feature of this water mass is a section referred to as the sub-surface layer. It is a product of Atlantic water that enters through canyons and is subjected to intense mixing on the Siberian Shelf. As it is entrained, it cools and acts a heat shield for the surface layer on account of weak mixing between layers.
However, over the past couple of decades a combination of the warming and the shoaling of Atlantic water are leading to the increasing influence of Atlantic water heat in melting sea ice in the eastern Arctic. The most recent estimates, for 2016–2018, indicate the oceanic heat flux to the surface has now overtaken the atmospheric flux in the eastern Eurasian Basin. Over the same period the weakening halocline stratification has coincided with increasing upper ocean currents thought to be associated with declining sea ice, indicate increasing mixing in this region. In contrast direct measurements of mixing in the western Arctic indicate the Atlantic water heat remains isolated at intermediate depths even under the 'perfect storm' conditions of the
This water is met by Greenland Sea Deep Water, which forms during the passage of winter storms. As temperatures cool dramatically in the winter, ice forms, and intense vertical convection allows the water to become dense enough to sink below the warm saline water below. Arctic Bottom Water is critically important because of its outflow, which contributes to the formation of Atlantic Deep Water. The overturning of this water plays a key role in global circulation and the moderation of climate.
In the depth range of is a water mass referred to as Atlantic Water. Inflow from the North Atlantic Current enters through the Fram Strait, cooling and sinking to form the deepest layer of the halocline, where it circles the Arctic Basin counter-clockwise. This is the highest volumetric inflow to the Arctic Ocean, equalling about 10 times that of the Pacific inflow, and it creates the Arctic Ocean Boundary Current. It flows slowly, at about 0.02 m/s. Atlantic Water has the same salinity as Arctic Bottom Water but is much warmer (up to ). In fact, this water mass is actually warmer than the surface water and remains submerged only due to the role of salinity in density. When water reaches the basin, it is pushed by strong winds into a large circular current called the Beaufort Gyre. Water in the Beaufort Gyre is far less saline than that of the Chukchi Sea due to inflow from large Canadian and Siberian rivers.
The final defined water mass in the Arctic Ocean is called Arctic Surface Water and is found in the depth range of . The most important feature of this water mass is a section referred to as the sub-surface layer. It is a product of Atlantic water that enters through canyons and is subjected to intense mixing on the Siberian Shelf. As it is entrained, it cools and acts a heat shield for the surface layer on account of weak mixing between layers.
However, over the past couple of decades a combination of the warming and the shoaling of Atlantic water are leading to the increasing influence of Atlantic water heat in melting sea ice in the eastern Arctic. The most recent estimates, for 2016–2018, indicate the oceanic heat flux to the surface has now overtaken the atmospheric flux in the eastern Eurasian Basin. Over the same period the weakening halocline stratification has coincided with increasing upper ocean currents thought to be associated with declining sea ice, indicate increasing mixing in this region. In contrast direct measurements of mixing in the western Arctic indicate the Atlantic water heat remains isolated at intermediate depths even under the 'perfect storm' conditions of the Great Arctic Cyclone of 2012
The Great Arctic Cyclone, or "Great Arctic Cyclone of 2012," was a powerful extratropical cyclone that was centered on the Arctic Ocean in early August 2012. Cyclones of this magnitude are rare in the Arctic summer, although common in the winter. ...
.
Waters originating in the Pacific and Atlantic both exit through the Fram Strait between Greenland and Svalbard Island, which is about deep and wide. This outflow is about 9 Sv. The width of the Fram Strait is what allows for both inflow and outflow on the Atlantic side of the Arctic Ocean. Because of this, it is influenced by the Coriolis force
In physics, the Coriolis force is an inertial or fictitious force that acts on objects in motion within a frame of reference that rotates with respect to an inertial frame. In a reference frame with clockwise rotation, the force acts to the ...
, which concentrates outflow to the East Greenland Current on the western side and inflow to the Norwegian Current
The Norwegian Current (also known as the Norway Coastal Current) is one of two dominant arctic inflows of water. It can be traced from near Shetland, north of Scotland, otherwise from the eastern North Sea at depths of up to 100 metres. It finally ...
on the eastern side. Pacific water also exits along the west coast of Greenland and the Hudson Strait (1–2 Sv), providing nutrients to the Canadian Archipelago.
As noted, the process of ice formation and movement is a key driver in Arctic Ocean circulation and the formation of water masses. With this dependence, the Arctic Ocean experiences variations due to seasonal changes in sea ice cover. Sea ice movement is the result of wind forcing, which is related to a number of meteorological conditions that the Arctic experiences throughout the year. For example, the Beaufort High—an extension of the Siberian High system—is a pressure system that drives the anticyclonic motion of the Beaufort Gyre. During the summer, this area of high pressure is pushed out closer to its Siberian and Canadian sides. In addition, there is a sea level pressure (SLP) ridge over Greenland that drives strong northerly winds through the Fram Strait, facilitating ice export. In the summer, the SLP contrast is smaller, producing weaker winds. A final example of seasonal pressure system movement is the low pressure system that exists over the Nordic and Barents Seas. It is an extension of the Icelandic Low, which creates cyclonic ocean circulation in this area. The low shifts to centre over the North Pole in the summer. These variations in the Arctic all contribute to ice drift reaching its weakest point during the summer months. There is also evidence that the drift is associated with the phase of the Arctic Oscillation and Atlantic Multidecadal Oscillation.
Sea ice
 Much of the Arctic Ocean is covered by sea ice that varies in extent and thickness seasonally. The mean extent of the Arctic sea ice has been continuously decreasing in the last decades, declining at a rate of currently 12.85% per decade since 1980 from the average winter value of . The seasonal variations are about , with the maximum in April and minimum in September. The sea ice is affected by wind and ocean currents, which can move and rotate very large areas of ice. Zones of compression also arise, where the ice piles up to form pack ice.
Much of the Arctic Ocean is covered by sea ice that varies in extent and thickness seasonally. The mean extent of the Arctic sea ice has been continuously decreasing in the last decades, declining at a rate of currently 12.85% per decade since 1980 from the average winter value of . The seasonal variations are about , with the maximum in April and minimum in September. The sea ice is affected by wind and ocean currents, which can move and rotate very large areas of ice. Zones of compression also arise, where the ice piles up to form pack ice.
Iceberg
An iceberg is a piece of freshwater ice more than 15 m long that has broken off a glacier or an ice shelf and is floating freely in open (salt) water. Smaller chunks of floating glacially-derived ice are called "growlers" or "bergy bits". The ...
s occasionally break away from northern Ellesmere Island
Ellesmere Island ( iu, script=Latn, Umingmak Nuna, lit=land of muskoxen; french: île d'Ellesmere) is Canada's northernmost and List of Canadian islands by area, third largest island, and the List of islands by area, tenth largest in the world. ...
, and icebergs are formed from glaciers in western Greenland and extreme northeastern Canada. Icebergs are not sea ice but may become embedded in the pack ice. Icebergs pose a hazard to ships, of which the ''Titanic'' is one of the most famous. The ocean is virtually icelocked from October to June, and the superstructure
A superstructure is an upward extension of an existing structure above a baseline. This term is applied to various kinds of physical structures such as buildings, bridges, or ships.
Aboard ships and large boats
On water craft, the superstruct ...
of ships are subject to icing from October to May. Before the advent of modern icebreakers, ships sailing the Arctic Ocean risked being trapped or crushed by sea ice (although the ''Baychimo
SS ''Baychimo'' was a steel-hulled 1,322 ton cargo steamer built in 1914 in Sweden and owned by the Hudson's Bay Company, used to trade provisions for pelts in Inuit settlements along the Victoria Island coast of the Northwest Territories of Canad ...
'' drifted through the Arctic Ocean untended for decades despite these hazards).
Climate
The Arctic Ocean is contained in apolar climate
The polar climate regions are characterized by a lack of warm summers but with varying winters. Every month in a polar climate has an average temperature of less than . Regions with polar climate cover more than 20% of the Earth's area. Most of ...
characterized by persistent cold and relatively narrow annual temperature ranges. Winters are characterized by the polar night, extreme cold, frequent low-level temperature inversions, and stable weather conditions. Cyclone
In meteorology, a cyclone () is a large air mass that rotates around a strong center of low atmospheric pressure, counterclockwise in the Northern Hemisphere and clockwise in the Southern Hemisphere as viewed from above (opposite to an anti ...
s are only common on the Atlantic side. Summers are characterized by continuous daylight
Daylight is the combination of all direct and indirect sunlight during the daytime. This includes direct sunlight, diffuse sky radiation, and (often) both of these reflected by Earth and terrestrial objects, like landforms and buildings. Sunligh ...
( midnight sun), and air temperatures can rise slightly above . Cyclones are more frequent in summer and may bring rain or snow. It is cloudy year-round, with mean cloud cover ranging from 60% in winter to over 80% in summer.
The temperature of the surface water of the Arctic Ocean is fairly constant at approximately , near the freezing point of seawater.
The density of sea water, in contrast to fresh water, increases as it nears the freezing point and thus it tends to sink. It is generally necessary that the upper of ocean water cools to the freezing point for sea ice to form. In the winter, the relatively warm ocean water exerts a moderating influence, even when covered by ice. This is one reason why the Arctic does not experience the extreme temperatures seen on the Antarctic continent.
There is considerable seasonal variation in how much pack ice of the Arctic ice pack covers the Arctic Ocean. Much of the Arctic ice pack is also covered in snow for about 10 months of the year. The maximum snow cover is in March or April—about over the frozen ocean.
The climate of the Arctic region has varied significantly during the Earth's history. During the Paleocene–Eocene Thermal Maximum
The Paleocene–Eocene thermal maximum (PETM), alternatively (ETM1), and formerly known as the "Initial Eocene" or "", was a time period with a more than 5–8 °C global average temperature rise across the event. This climate event o ...
55 million years ago, when the global climate underwent a warming of approximately , the region reached an average annual temperature of . The surface waters of the northernmost Arctic Ocean warmed, seasonally at least, enough to support tropical lifeforms (the dinoflagellate
The dinoflagellates (Greek δῖνος ''dinos'' "whirling" and Latin ''flagellum'' "whip, scourge") are a monophyletic group of single-celled eukaryotes constituting the phylum Dinoflagellata and are usually considered algae. Dinoflagellates are ...
s ''Apectodinium augustum'') requiring surface temperatures of over .
Currently, the Arctic region is warming twice as fast as the rest of the planet.
Biology
 Due to the pronounced seasonality of 2–6 months of midnight sun and polar night in the Arctic Ocean, the primary production of photosynthesizing organisms such as ice algae and
Due to the pronounced seasonality of 2–6 months of midnight sun and polar night in the Arctic Ocean, the primary production of photosynthesizing organisms such as ice algae and phytoplankton
Phytoplankton () are the autotrophic (self-feeding) components of the plankton community and a key part of ocean and freshwater ecosystems. The name comes from the Greek words (), meaning 'plant', and (), meaning 'wanderer' or 'drifter'.
Ph ...
is limited to the spring and summer months (March/April to September). Important consumers of primary producers in the central Arctic Ocean and the adjacent shelf seas include zooplankton, especially copepod
Copepods (; meaning "oar-feet") are a group of small crustaceans found in nearly every freshwater and saltwater habitat (ecology), habitat. Some species are planktonic (inhabiting sea waters), some are benthos, benthic (living on the ocean floor) ...
s ('' Calanus finmarchicus'', '' Calanus glacialis'', and '' Calanus hyperboreus'') and euphausiids, as well as ice-associated fauna (e.g., amphipods). These primary consumers form an important link between the primary producers and higher trophic levels. The composition of higher trophic levels in the Arctic Ocean varies with region (Atlantic side vs. Pacific side) and with the sea-ice cover. Secondary consumer
A carnivore , or meat-eater (Latin, ''caro'', genitive ''carnis'', meaning meat or "flesh" and ''vorare'' meaning "to devour"), is an animal or plant whose food and energy requirements derive from animal tissues (mainly muscle, fat and other sof ...
s in the Barents Sea, an Atlantic-influenced Arctic shelf sea, are mainly sub-Arctic species including herring
Herring are forage fish, mostly belonging to the family of Clupeidae.
Herring often move in large schools around fishing banks and near the coast, found particularly in shallow, temperate waters of the North Pacific and North Atlantic Oceans, i ...
, young cod, and capelin. In ice-covered regions of the central Arctic Ocean, polar cod is a central predator of primary consumers. The apex predators in the Arctic Ocean— marine mammals such as seals, whales, and polar bear
The polar bear (''Ursus maritimus'') is a hypercarnivorous bear whose native range lies largely within the Arctic Circle, encompassing the Arctic Ocean, its surrounding seas and surrounding land masses. It is the largest extant bear specie ...
s—prey upon fish.
Endangered marine species in the Arctic Ocean include walruses and whales. The area has a fragile ecosystem, and it is especially exposed to climate change, because it warms faster than the rest of the world. Lion's mane jellyfish are abundant in the waters of the Arctic, and the banded gunnel is the only species of gunnel that lives in the ocean.


Natural resources
Petroleum and natural gas fields, placer deposits,polymetallic nodules
Polymetallic nodules, also called manganese nodules, are mineral concretions on the sea bottom formed of concentric layers of iron and manganese hydroxides around a core. As nodules can be found in vast quantities, and contain valuable metals, dep ...
, sand and gravel aggregates, fish, seals and whales can all be found in abundance in the region.
The political dead zone near the centre of the sea is also the focus of a mounting dispute between the United States, Russia, Canada, Norway, and Denmark. It is significant for the global energy market because it may hold 25% or more of the world's undiscovered oil and gas resources.
Environmental concerns
Arctic ice melting
TheArctic ice pack
The Arctic ice pack is the sea ice cover of the Arctic Ocean and its vicinity. The Arctic ice pack undergoes a regular seasonal cycle in which ice melts in spring and summer, reaches a minimum around mid-September, then increases during fall a ...
is thinning, and a seasonal hole in the ozone layer
The ozone layer or ozone shield is a region of Earth's stratosphere that absorbs most of the Sun's ultraviolet radiation. It contains a high concentration of ozone (O3) in relation to other parts of the atmosphere, although still small in rela ...
frequently occurs. Reduction of the area of Arctic sea ice reduces the planet's average albedo, possibly resulting in global warming in a positive feedback mechanism.Earth – melting in the heat?Richard Black, 7 October 2005. BBC News. Retrieved 7 December 2006. Research shows that the Arctic may become ice-free in the summer for the first time in human history by 2040. Estimates vary for when the last time the Arctic was ice-free: 65 million years ago when fossils indicate that plants existed there to as recently as 5,500 years ago; ice and ocean cores going back 8,000 years to the last warm period or 125,000 during the last intraglacial period. Warming temperatures in the Arctic may cause large amounts of fresh melt-water to enter the north Atlantic, possibly disrupting global ocean current patterns. Potentially severe changes in the Earth's climate might then ensue. As the extent of sea ice diminishes and sea level rises, the effect of storms such as the
Great Arctic Cyclone of 2012
The Great Arctic Cyclone, or "Great Arctic Cyclone of 2012," was a powerful extratropical cyclone that was centered on the Arctic Ocean in early August 2012. Cyclones of this magnitude are rare in the Arctic summer, although common in the winter. ...
on open water increases, as does possible salt-water damage to vegetation on shore at locations such as the Mackenzie Delta as stronger storm surge
A storm surge, storm flood, tidal surge, or storm tide is a coastal flood or tsunami-like phenomenon of rising water commonly associated with low-pressure weather systems, such as cyclones. It is measured as the rise in water level above the n ...
s become more likely.
Global warming has increased encounters between polar bear
The polar bear (''Ursus maritimus'') is a hypercarnivorous bear whose native range lies largely within the Arctic Circle, encompassing the Arctic Ocean, its surrounding seas and surrounding land masses. It is the largest extant bear specie ...
s and humans. Reduced sea ice due to melting is causing polar bears to search for new sources of food. Beginning in December 2018 and coming to an apex in February 2019, a mass invasion of polar bears into the archipelago of Novaya Zemlya
Novaya Zemlya (, also , ; rus, Но́вая Земля́, p=ˈnovəjə zʲɪmˈlʲa, ) is an archipelago in northern Russia. It is situated in the Arctic Ocean, in the extreme northeast of Europe, with Cape Flissingsky, on the northern island, ...
caused local authorities to declare a state of emergency. Dozens of polar bears were seen entering homes, public buildings and inhabited areas.
Clathrate breakdown
Sea ice
Sea ice arises as seawater freezes. Because ice is less dense than water, it floats on the ocean's surface (as does fresh water ice, which has an even lower density). Sea ice covers about 7% of the Earth's surface and about 12% of the world's oce ...
, and the cold conditions it sustains, serves to stabilize methane deposits on and near the shoreline, preventing the clathrate breaking down and outgassing methane into the atmosphere, causing further warming. Melting of this ice may release large quantities of methane, a powerful greenhouse gas
A greenhouse gas (GHG or GhG) is a gas that Absorption (electromagnetic radiation), absorbs and Emission (electromagnetic radiation), emits radiant energy within the thermal infrared range, causing the greenhouse effect. The primary greenhouse ...
, into the atmosphere
An atmosphere () is a layer of gas or layers of gases that envelop a planet, and is held in place by the gravity of the planetary body. A planet retains an atmosphere when the gravity is great and the temperature of the atmosphere is low. A s ...
, causing further warming in a strong positive feedback cycle and marine genera and species to become extinct.
Other concerns
Other environmental concerns relate to the radioactive contamination of the Arctic Ocean from, for example, Russian radioactive waste dump sites in the Kara Sea,Cold War
The Cold War is a term commonly used to refer to a period of geopolitical tension between the United States and the Soviet Union and their respective allies, the Western Bloc and the Eastern Bloc. The term '' cold war'' is used because the ...
nuclear test sites such as Novaya Zemlya, Camp Century's contaminants in Greenland, and radioactive contamination from the Fukushima Daiichi nuclear disaster
The was a nuclear accident in 2011 at the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant in Ōkuma, Fukushima, Japan. The proximate cause of the disaster was the 2011 Tōhoku earthquake and tsunami, which occurred on the afternoon of 11 March 2011 and ...
.
On 16 July 2015, five nations (United States, Russia, Canada, Norway, Denmark/Greenland) signed a declaration committing to keep their fishing vessels out of a 1.1 million square mile zone in the central Arctic Ocean near the North Pole. The agreement calls for those nations to refrain from fishing there until there is better scientific knowledge about the marine resources and until a regulatory system is in place to protect those resources.
See also
* Arctic Bridge *Arctic cooperation and politics
Arctic cooperation and politics are partially coordinated via the Arctic Council, composed of the eight Arctic nations: the United States, Canada, Iceland, Norway, Sweden, Finland, Russia, and Denmark with Greenland and the Faroe Islands. The domi ...
* Extreme points of the Arctic
* International Arctic Science Committee
* List of rivers of the Americas by coastline
* Nordicity
* Seven Seas
* Subarctic
The subarctic zone is a region in the Northern Hemisphere immediately south of the true Arctic, north of humid continental regions and covering much of Alaska, Canada, Iceland, the north of Scandinavia, Siberia, and the Cairngorms. Generally, ...
References
Further reading
* Neatby, Leslie H., ''Discovery in Russian and Siberian Waters'' (1973), . * Ray, L., and B. Bacon, eds., ''The Arctic Ocean'' (1982), . * Thorén, Ragnar V.A., ''Picture Atlas of the Arctic'' (1969), .External links
Arctic Council
Arctic Environmental Atlas
Interactive map
Arctic Great Rivers Observatory (ArcticGRO)
Arctic Ocean
'' The World Factbook''. Central Intelligence Agency.
Daily Arctic Ocean Rawinsonde Data from Soviet Drifting Ice Stations (1954–1990)
at NSIDC
Images from Web Cams deployed in spring on an ice floe
Data from instruments deployed on an ice floe
International Polar Foundation
* {{Authority control several islands Oceans Extreme points of Earth Articles containing video clips Geography of Northeast Asia Geography of Northern Europe Geography of Eastern Europe Geography of North America Seas of the United States Seas of Canada Seas of Greenland Seas of Norway Seas of Russia